Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: Understanding HVAC TCO
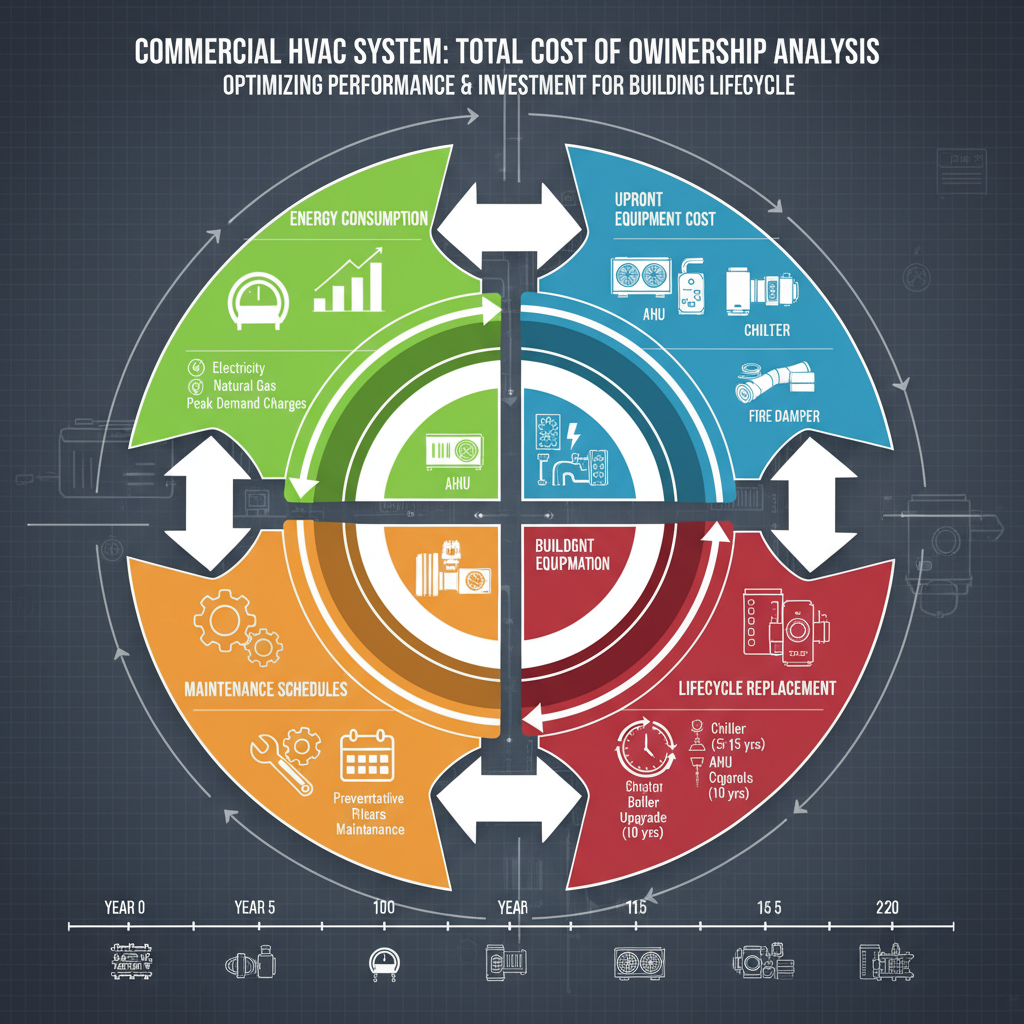
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for commercial HVAC systems includes:
- Initial equipment and installation costs
- Energy consumption over system life
- Maintenance, repair, and replacement expenses
A proper TCO analysis allows building owners and engineers to balance upfront investment with long-term operational efficiency.
Key Components of HVAC TCO
Equipment and Installation Costs
- Initial cost of air handling units, chillers, boilers, fans, and ductwork
- Cost of fire dampers, smoke control devices, and controls
- Installation labor and commissioning expenses
Energy Consumption and Operating Costs
- Electricity for fans, pumps, and compressors
- Gas or other fuels for heating systems
- Seasonal and peak load considerations for energy efficiency
Maintenance and Lifecycle Expenses
- Regular inspection, cleaning, and filter replacement
- Predictive maintenance with smart building automation systems (BMS)
- Replacement or repair of components reaching end-of-life
Downtime and Operational Risk
- Loss of productivity due to system failure
- Emergency repair costs and contractor response fees
- Impact on occupant comfort and indoor air quality
Strategies to Optimize HVAC TCO
Selecting Energy-Efficient Equipment
- Use high-efficiency chillers, VAV systems, and variable-speed fans
- Incorporate ERV/HRV units to reduce heating/cooling loads
- Choose durable, low-maintenance components
Implementing Smart Controls
- Use BMS and IoT sensors for predictive maintenance
- Optimize setpoints, scheduling, and occupancy-based ventilation
- Monitor energy consumption in real-time to reduce waste
Lifecycle Planning and Replacement Strategy
- Analyze component lifespan and replacement schedules
- Budget for planned upgrades and retrofits
- Avoid costly emergency replacements by proactive planning
Image Reference (for Blog Integration)
Image Alt Text:
Diagram illustrating total cost of ownership analysis for a commercial HVAC system, including energy consumption, maintenance, and lifecycle costs.
Image Title:
Commercial HVAC Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Conclusion: Making Informed HVAC Investment Decisions
A comprehensive TCO analysis helps building owners and engineers:
- Optimize capital expenditure vs operational efficiency
- Reduce energy use and maintenance costs over time
- Maintain occupant comfort, safety, and system reliability
YAOAN provides engineering support and high-efficiency HVAC solutions to maximize TCO benefits in commercial and industrial buildings.
FAQ – HVAC TCO
What is HVAC Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)?
TCO is the sum of all costs associated with purchasing, installing, operating, maintaining, and eventually replacing an HVAC system over its lifecycle.
How can energy efficiency reduce TCO?
Energy-efficient systems lower utility bills, reduce peak load costs, and extend equipment lifespan, reducing total ownership costs over time.
Why is maintenance planning important for TCO?
Proactive maintenance prevents costly breakdowns, extends component life, and ensures HVAC systems operate efficiently and safely.