Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: The IAQ-Energy Dilemma
Maintaining healthy indoor air quality (IAQ) often requires increased ventilation, filtration, and air exchange rates. However, higher ventilation can lead to:
- Increased energy consumption
- Higher operating costs
- Greater carbon footprint
Balancing IAQ and energy efficiency is critical for modern, sustainable building design.
Key Trade-Off Considerations
Ventilation Rate vs Energy Use
- Higher fresh air rates improve IAQ but increase heating/cooling loads
- Optimize demand-controlled ventilation (DCV) to reduce unnecessary energy use
- Consider occupancy-based airflow adjustments
Filtration vs Fan Power
- Advanced HEPA or MERV filters improve air cleanliness
- High-efficiency filters increase pressure drop, requiring more fan energy
- Balance filtration performance with fan energy and system capacity
Temperature and Humidity Control
- Tight temperature and humidity control improves comfort and IAQ
- Over-conditioning air may waste energy, while under-conditioning reduces comfort
- Use smart sensors and BMS to maintain optimal setpoints efficiently
System Zoning and Air Distribution
- Zoning allows targeted airflow, improving IAQ where needed
- Reduces energy waste in unoccupied zones
- Proper air distribution and balancing ensures both comfort and energy efficiency
Strategies to Optimize IAQ and Energy Use
Smart Controls and Automation
- Implement BMS with IAQ monitoring
- Use CO₂ sensors to adjust ventilation dynamically
- Enable predictive control for peak efficiency
Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV/HRV)
- Recover heat or coolness from exhaust air
- Reduce energy needed to condition incoming fresh air
- Maintain high ventilation rates without excessive energy penalty
Filter and Maintenance Optimization
- Select filters with low pressure drop but high efficiency
- Schedule regular maintenance to maintain airflow and IAQ
- Monitor fan performance to avoid unnecessary energy use
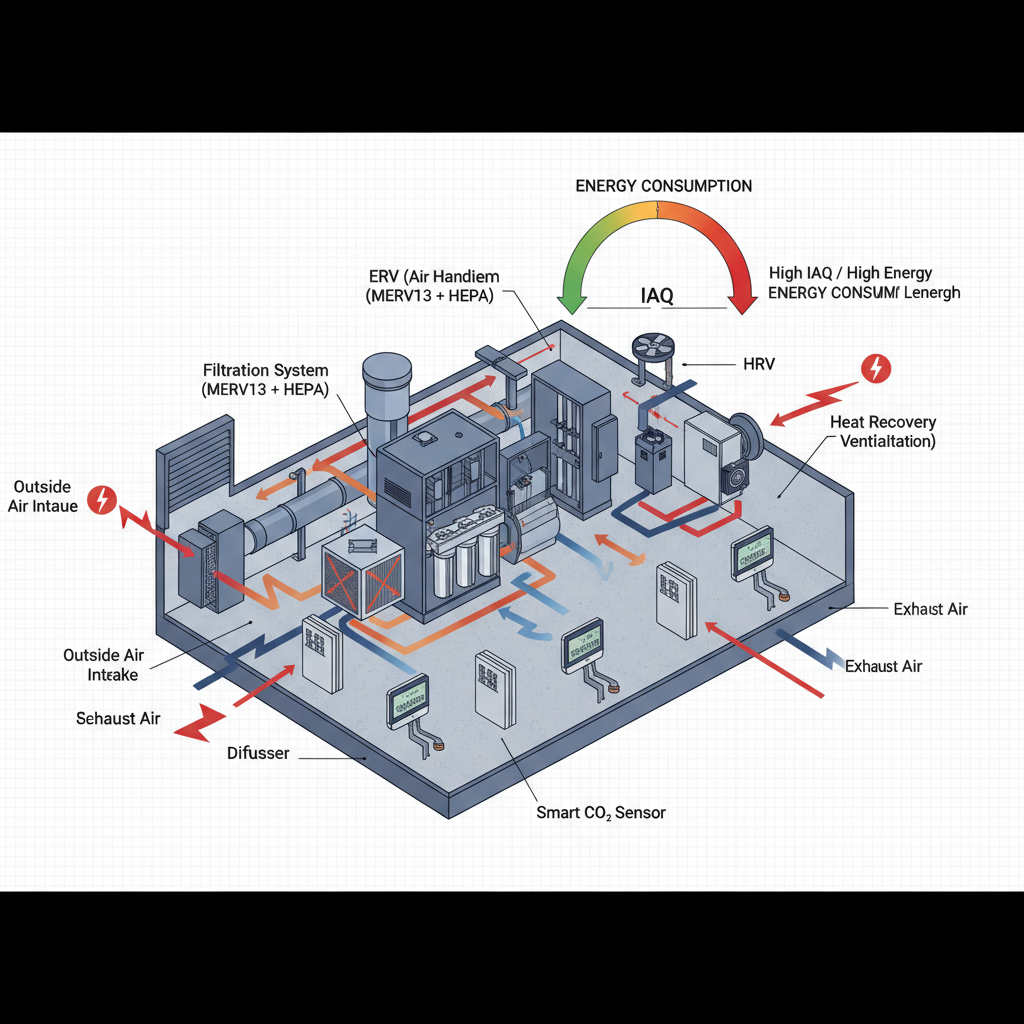
Image Reference (for Blog Integration)
Image Alt Text:
Diagram showing the trade-off between indoor air quality and energy consumption in a commercial building HVAC system with smart controls and airflow distribution.
Image Title:
Indoor Air Quality vs Energy Consumption in HVAC Systems
Conclusion: Achieving the Right Balance
Optimizing IAQ and energy consumption requires:
- Intelligent ventilation strategies
- Efficient filtration and airflow distribution
- Smart automation to dynamically adjust system operation
YAOAN provides HVAC solutions that help buildings maintain healthy air while minimizing energy use, ensuring sustainable performance and occupant comfort.
FAQ – IAQ vs Energy Consumption
How does increasing ventilation affect energy use?
Higher ventilation rates improve IAQ but increase heating, cooling, and fan energy, raising operating costs.
What technologies help balance IAQ and energy efficiency?
Demand-controlled ventilation, energy recovery ventilators (ERV/HRV), smart BMS, and occupancy-based controls help maintain air quality while minimizing energy use.
Can filtration affect energy consumption?
Yes. High-efficiency filters reduce contaminants but increase pressure drop, requiring more fan energy. Proper filter selection balances efficiency and energy.