Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
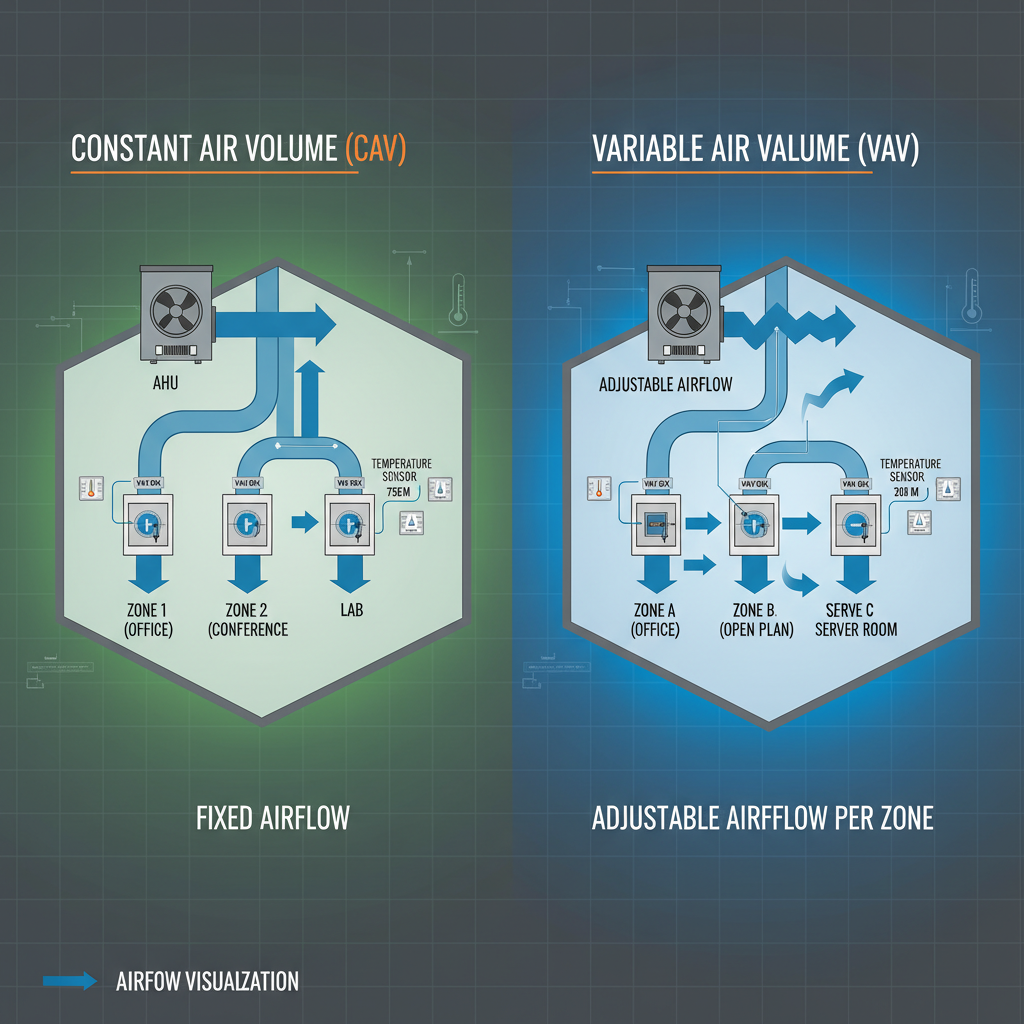
HVAC system design often requires choosing between Constant Air Volume (CAV) and Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems. Each approach has unique benefits, limitations, and applications:
- CAV Systems: Deliver a fixed airflow regardless of zone demand
- VAV Systems: Adjust airflow dynamically based on occupancy and thermal load
Understanding the differences is critical for energy efficiency, comfort, and regulatory compliance. YAOAN Ventilation provides expert guidance and solutions for both system types.
Constant Air Volume (CAV) Systems
Key Features
- Delivers a fixed airflow rate to each zone
- Temperature is controlled by heating or cooling the air, not by adjusting volume
- Simple design and easy installation
Advantages
- Low initial cost and straightforward control
- Stable airflow simplifies coordination with fire and smoke dampers
- Suitable for single-zone applications
Limitations
- Higher energy consumption due to constant fan operation
- Less efficient in multi-zone buildings with variable loads
- Potential discomfort when thermal loads fluctuate
Variable Air Volume (VAV) Systems
Key Features
- Adjusts airflow to match demand in each zone
- Maintains comfort while minimizing energy use
- Uses VAV boxes, dampers, sensors, and central AHU
Advantages
- Significant energy savings (20–50% fan energy reduction)
- Optimized comfort for multi-zone buildings
- Integrates with smart building management and demand-controlled ventilation
Limitations
- Higher initial cost and more complex control systems
- Requires careful sensor placement and calibration
- Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance
Technical Comparison
| Feature | CAV System | VAV System |
|---|---|---|
| Airflow Control | Constant | Variable per zone |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Comfort | Fixed, may be uneven | Optimized per zone |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | Low | High |
| Maintenance | Simple | Requires regular calibration |
| Best Application | Single-zone or uniform load buildings | Multi-zone, variable load buildings |
Design Considerations
System Selection
- Evaluate building occupancy patterns and thermal load variability
- Consider energy savings vs. installation cost
Controls and Automation
- CAV: Simple thermostats or zone controllers
- VAV: Sensors, actuators, BMS integration, DCV capability
Maintenance and Lifecycle
- Schedule inspections for dampers, actuators, and sensors
- Document system performance and energy savings
FAQ
What is the main difference between CAV and VAV systems?
CAV delivers a constant airflow to each zone, while VAV adjusts airflow based on demand, optimizing energy use and comfort.
Which system is more energy-efficient?
VAV systems are more energy-efficient, especially in multi-zone buildings with variable occupancy and thermal loads.
Are CAV systems still relevant?
Yes, for single-zone buildings or spaces with uniform load requirements, CAV systems can be cost-effective and simple to operate.
Can YAOAN provide both CAV and VAV solutions?
Yes, YAOAN designs, supplies, and supports both CAV and VAV systems, ensuring compliance, efficiency, and comfort for commercial and industrial buildings.
About YAOAN Ventilation
YAOAN Ventilation offers comprehensive HVAC solutions including CAV and VAV systems, VAV boxes, dampers, sensors, and building automation integration. Our expertise ensures energy-efficient, compliant, and reliable HVAC systems for offices, hospitals, airports, and industrial facilities worldwide.