Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Sustainable building design emphasizes energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and environmental responsibility. HVAC systems are central to achieving these goals. Poorly designed systems can lead to:
- High energy consumption
- Inefficient airflow and uneven temperatures
- Increased operational costs
- Reduced system lifespan
Energy-efficient HVAC design integrates advanced technologies, smart controls, and careful planning to maximize performance while minimizing energy use.
Key Strategies for Energy-Efficient HVAC Design
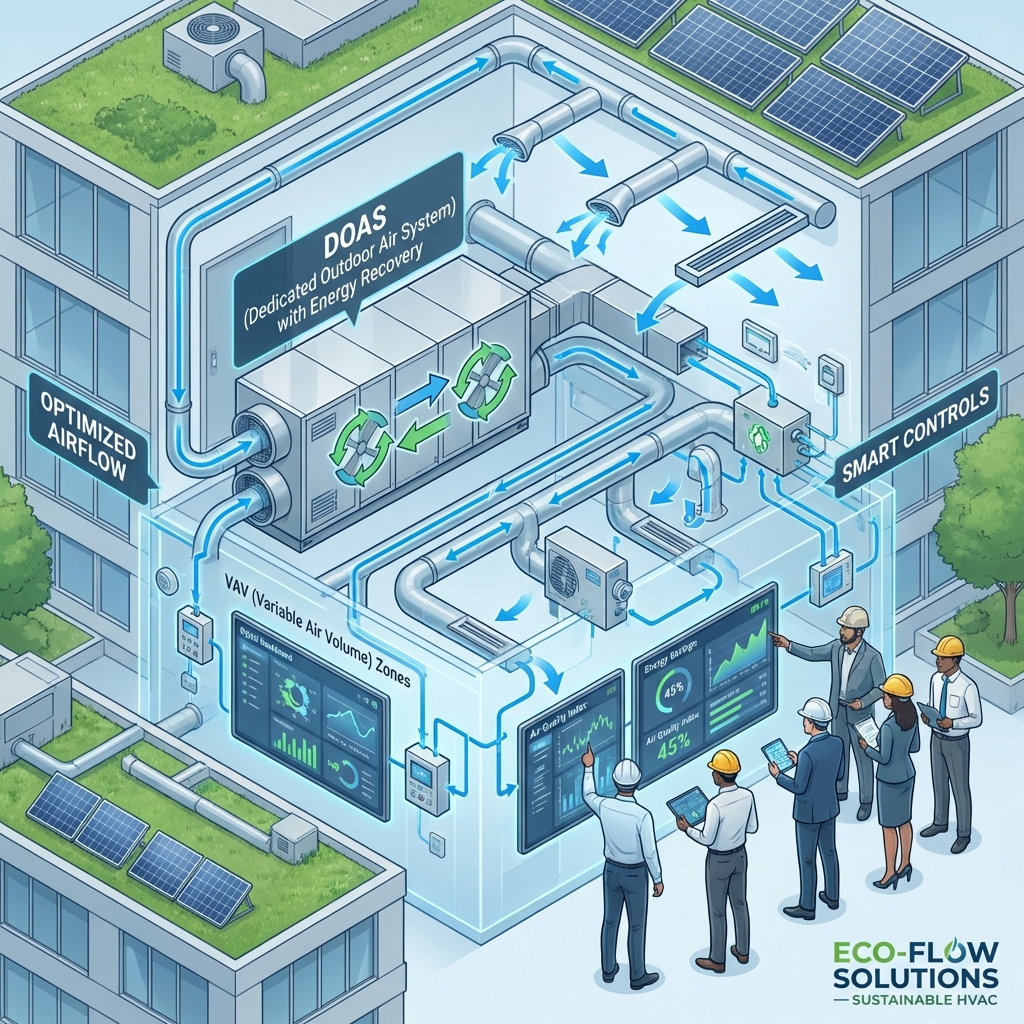
Variable Air Volume (VAV) and Dedicated Outdoor Air Systems (DOAS)
Benefits:
- Supply air tailored to actual occupancy and load requirements
- Reduced fan and cooling energy
- Improved indoor air quality through controlled ventilation
Implementation Tips:
- Use VAV boxes to adjust airflow per zone
- Integrate DOAS units for precise outdoor air treatment
- Balance energy savings with comfort and indoor air standards
Smart Controls and Building Automation
Benefits:
- Real-time monitoring and adjustment of temperature, humidity, and airflow
- Peak load management and energy optimization
- Predictive maintenance alerts to reduce downtime
Implementation Tips:
- Deploy IoT-enabled sensors and controls
- Program schedules based on occupancy patterns
- Monitor system performance through dashboards for informed decisions
Optimized Air Distribution and Diffuser Selection
Benefits:
- Uniform comfort across all occupied zones
- Minimized hot/cold spots and drafts
- Reduced fan energy by avoiding over-pressurization
Implementation Tips:
- Conduct CFD simulations for airflow planning
- Select jet nozzle diffusers, ceiling or slot diffusers depending on space requirements
- Adjust placement to accommodate architectural constraints
Energy Recovery and Sustainable Equipment
Benefits:
- Heat recovery reduces heating and cooling energy
- High-efficiency chillers, fans, and pumps lower operational costs
- Compliance with green building standards (LEED, BREEAM, WELL)
Implementation Tips:
- Implement energy recovery ventilators (ERV) or heat exchangers
- Choose high-efficiency motors and variable speed drives
- Optimize duct layouts to minimize pressure losses
Best Practices for Sustainable HVAC Design
Early Design Integration
- Collaborate with architects, structural, and electrical engineers
- Include HVAC considerations during early building modeling and BIM planning
Regular Commissioning and Performance Verification
- Validate airflow, temperature, and energy consumption post-installation
- Ensure fire and smoke safety systems function correctly alongside energy-efficient systems
Lifecycle Cost Considerations
- Evaluate total cost of ownership including energy, maintenance, and equipment replacement
- Plan for upgrades that improve efficiency over time
FAQ
What makes HVAC design energy-efficient?
Using VAV/DOAS systems, optimized air distribution, smart controls, and high-efficiency equipment reduces energy consumption while maintaining comfort.
How can airflow be optimized in sustainable buildings?
Through careful diffuser selection, CFD modeling, and balancing air distribution across all zones.
What role do smart controls play in HVAC energy efficiency?
They monitor real-time performance, adjust system parameters, reduce peak energy loads, and provide predictive maintenance alerts.
How does energy recovery improve HVAC efficiency?
By reusing heat or cooling from exhaust air, reducing the load on heating and cooling equipment and saving operational energy.
About YAOAN Ventilation
YAOAN Ventilation provides energy-efficient HVAC solutions for sustainable buildings. Our expertise covers VAV, DOAS, smart automation, optimized airflow, and energy recovery systems, enabling long-term cost savings, environmental sustainability, and occupant comfort in commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects.